指標的指標
指標的指標,意思是存指標的記憶體位址。
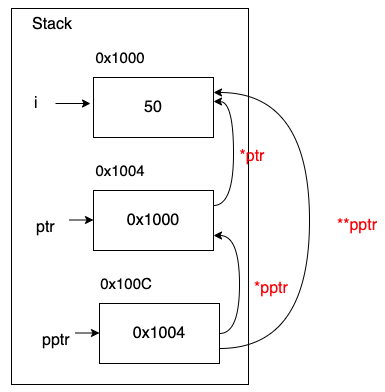
下圖中,有變數i的記憶體位址0x1000,存放50。
ptr本身的記憶體位址是0x1004,存放變數i的記憶體位址0x1000。
pptr本身的記憶體位址是0x100c,存放的指標ptr的記憶體位址0x1004。
對ptr存放的位址0x1000使用*取值運算子,可以取得50的數值。
對pptr存放的位址0x1004使用*取值運算子,可以取得ptr的位址。
對pptr存放的位址0x1004使用二次**取值運算子,取得50的數值,2次取值運算子,第1次取得ptr的位址,第2次取得50。
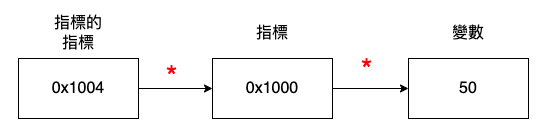
以下有點像鏈結串列,先從pptr存的位址,使用*取值運算子,得到ptr存的位址,使用*取值運算子,得到變數存放的數值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
int main() {
int i = 50;
int* ptr = &i;
int** pptr = &ptr;
printf("&i = %p \n", &i);
printf("&ptr = %p, ptr = %p, value = %d \n", &ptr, ptr, * ptr);
printf("&pptr = %p, pptr = %p, value = %d \n", &pptr, pptr, ** pptr);
return 0;
}
&i = 0x1000
&ptr = 0x1004, ptr = 0x1000, value = 50
&pptr = 0x100c, pptr = 0x1004, value = 50
指標的位址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
int main() {
int i = 40;
cout << "i的值 = " << i << ",i的位址 = " << &i << endl;
int *p = &i;
cout << "指標p指向的位址 = " << p << ",指標p的位址 = " << &p << ",指標p指向位址的值=" << *p << endl;
int **pp = &p;
cout << "指標pp指向的位址 = " << pp << ",指標pp的位址 = " << &pp << ",指標pp指向的位址(p)指向的位址(i)=" << *pp << endl;
cout << "指標pp指向的位址(p)指向的位址(i)的值=" << **pp << endl;
return 0;
}
i的值 = 40,i的位址 = 0x7ff7bfeff468
指標p指向的位址 = 0x7ff7bfeff468,指標p的位址 = 0x7ff7bfeff460,指標p指向位址的值=40
指標pp指向的位址 = 0x7ff7bfeff460,指標pp的位址 = 0x7ff7bfeff458,指標pp指向的位址(p)指向的位址(i)=0x7ff7bfeff468
指標pp指向的位址(p)指向的位址(i)的值=40
其它程式碼解釋
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
int main() {
int i4 = 40;
//宣告一個指標存i4的位址
int *p2 = &i4;
//將p2指標的位址傳給pp2
int **pp2 = &p2;
//1.把pp2存放的位址,使用取值運算子*,也就是指標p2的位址
//*pp2;
//2.再把p2位址,使用取值運算子*,也就是40
//**pp2
printf("解出pp2的值:%d\n",**pp2);
return 0;
}
執行結果
解出pp2的值:40
函式參數為指標的指標
在函式中若要修改指標所指向的記憶體位址,就要用到指標的指標。
引數為指標的位址,函式參數宣告為指標資料型態** 指標變數,這樣才可以接收指標的記憶體位址。
參考以下文章
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/passing-reference-to-a-pointer-in-c/
If a pointer is passed to a function as a parameter and tried to be modified then the changes made to the pointer does not reflects back outside that function. This is because only a copy of the pointer is passed to the function. It can be said that “pass by pointer” is passing a pointer by value. In most cases, this does not present a problem. But the problem comes when you modify the pointer inside the function. Instead of modifying the variable, you are only modifying a copy of the pointer and the original pointer remains unmodified.
(google翻譯)如果將指標作為參數傳遞給函式並嘗試對其進行修改,則對指標所做的更改不會反映回該函式外部。這是因為僅將指標的副本傳遞給函式。可以說「透過指標傳遞」就是按值傳遞指標。在大多數情況下,這不會出現問題。但當你修改函式內部的指標時,問題就來了。您只是修改指標的副本,而不是修改變數,而原始指標保持不變。
- 函式語法
傳回型態 函式名(指標資料型態** 指標) {
*指標 = 其它記憶體位址
}
- 呼叫函式語法
函式(&指標位址)
程式碼
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int global_var = 100;
void changePointerValue(int** ptr_ptr){
*ptr_ptr = &global_var; //改為指向global_var
}
int main() {
int var = 1;
int* pointer_to_var = &var; //指向var
cout << "Before:" << *pointer_to_var << endl;
//passing the address of the pointer
//把指標的位址傳進函式中
changePointerValue(&pointer_to_var);
cout << "After:" << *pointer_to_var << endl;
return 0;
}
Before:1
After:100
指標的指標與new
參考文章
new會返回動態配置記憶體的開始位址,將p_to_p使用*取值運算子修改p指向的位址。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//宣告一個函式initAddress() 指標是p_to_p,指向外部指標的位址
void initAddress(int** p_to_p){
//印出指向外部指標p的記憶體位址
cout << "Before p address = " << *p_to_p << endl;
//動態配置記憶體位址,位址存放的內容為10,使用new會返回動態配置記憶體的開始位址。
//使用*取值運算子修改指標p指向的位址
*p_to_p = new int(10);
//印出指向外部指標的記憶體位址與值
cout << "After p address= " << *p_to_p << ",After p value = " << **p_to_p << endl;
}
int main() {
//宣告指標p,初始化為nullptr,也就是沒有指向任何位址
int* p = nullptr;
//呼叫函式initAddress,引數為指標p的位址
initAddress(&p);
//印出指標p的位址,印出指標p指向的位址,對指向的位址取出內容。
cout << "== outside == " << endl;
cout << "outside pointer address = " << p << ",outside pointer value = " << *p << endl;
return 0;
}
Before p address = 0x0
After p address= 0x60000000c010,After p value = 10
== outside ==
outside pointer address = 0x60000000c010,outside pointer value = 10