霍夫曼樹
建立簡單霍夫曼樹
排序
未排序資料如下:
60, 5, 16, 24, 12
排序後:
5, 12, 16, 24, 60
取出2個最小元素
取出前面2個最小元素5、12,將2個元素的數值相加,並使用相加的值,建立新的節點。
新節點的左子樹指向5,右子樹指向12。
再把5,12從List中刪掉。
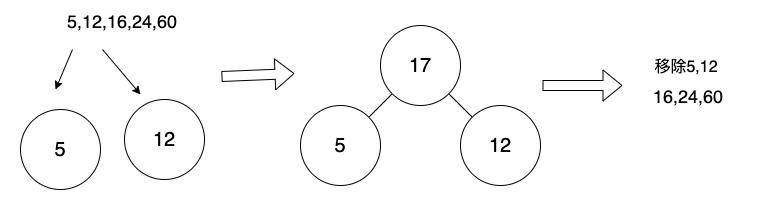
刪除5,12的List變成下方:
16, 24, 60
將剛才建立的17的新節點,加入List中。
增加17的List變成下方:
16, 17, 24, 60
將16, 17取出,將2個元素的數值相加,並使用相加的值,建立新的節點。
新節點的左子樹指向16,右子樹指向17。
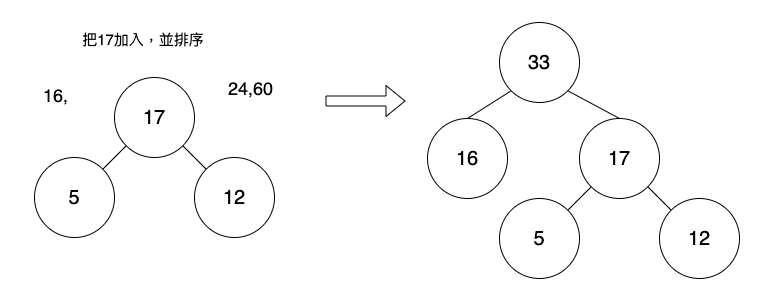
刪除16,17的List變成下方:
24, 60
將新節點33加入,並排序。
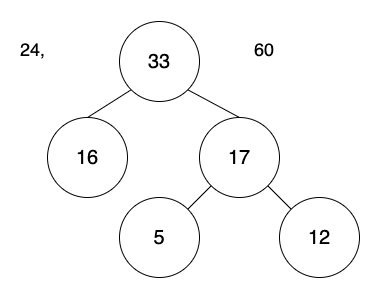
增加33的List變成下方:
24, 33, 60
將24, 33取出,將2個元素的數值相加,並使用相加的值,建立新的節點。
新節點的左子樹指向24,右子樹指向33。
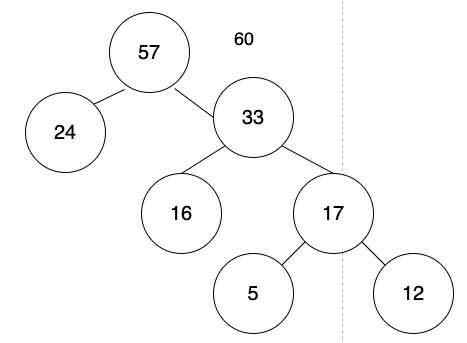
刪除24,33的List變成下方:
60
增加57的List變成下方:
57, 60
將57, 60取出,將2個元素的數值相加,並使用相加的值,建立新的節點。
新節點的左子樹指向57,右子樹指向60。
刪除57,60的List變成下方:
增加117的List變成下方:
117
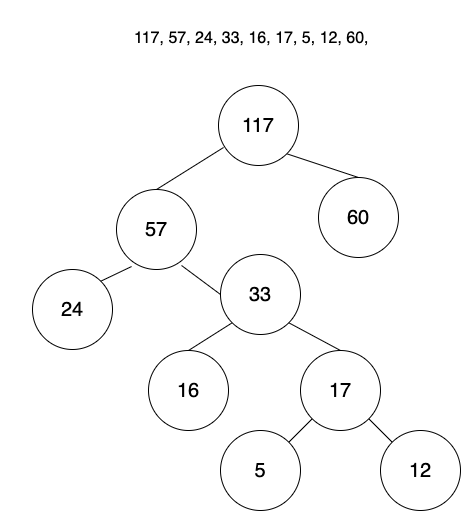
最後只剩下一個元素117,霍夫曼樹建立完畢。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class HuffmanBasic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
createHuffman();
}
public static void createHuffman() {
int[] data = {60,5,16,24,12};
List<HuffNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
// 建立節點
HuffNode node = new HuffNode(data[i]);
list.add(node);
}
// 迴圈的離開條件:只剩下一個元素
// 迴圈的進入條件:元素大於1個
while (list.size() > 1) {
// 排序,由小到大
Collections.sort(list);
// 取出最小的前面二個元素
HuffNode leftNode = list.get(0);
HuffNode rightNode = list.get(1);
// 將前面最小的二個元素值相加,產生新的節點
HuffNode parent = new HuffNode(leftNode.value + rightNode.value);
// 左節點、右節點為最小的前二個元素
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
// 移除最小的前二個元素
list.remove(leftNode);
list.remove(rightNode);
// 加入新的節點
list.add(parent);
}
// 取出唯一的節點,這個就是huffman霍夫曼樹,進行前序遍歷。
list.get(0).preOrder();
}
}
class HuffNode implements Comparable<HuffNode>{
public int value;
public HuffNode left;
public HuffNode right;
public HuffNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
/**
* 排序
* @param o the object to be compared.
* @return
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(HuffNode o) {
return this.value - o.value;
}
/**
* 前序
*/
public void preOrder() {
System.out.print(this.value + ", ");
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HuffNode{" +
"value=" + value +
'}';
}
}
117, 57, 24, 33, 16, 17, 5, 12, 60,
霍夫曼編碼
以下字串根據字元進行統計數量。
aabc
ASCII對映如下:
- a 97
- b 98
- c 99
統計結果如下:
| 字元 | ASCII | 數量 |
|---|---|---|
| a | 97 | 2 |
| b | 98 | 1 |
| c | 99 | 1 |
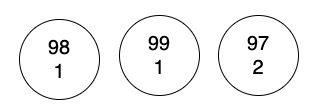
按照數量由小到大排序:
98(1), 99(1), 97(2)
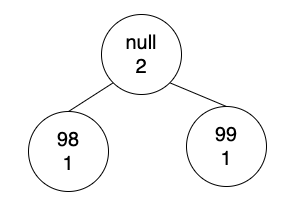
將前二個數量最小的,把98與99的數量相加,建立新的節點,新節點是null,數量為98、99的數量總合。
新節點的左子樹指向98,右子樹指向99。
把98、99的節點,從List刪除,把新節點放到List,根據數量排序。排序結果如下:
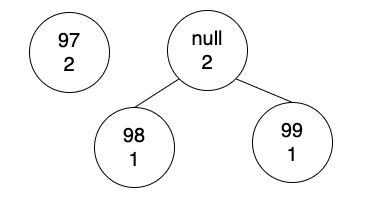
將list中前二個數量最小的,數量相加,建立新節點,新節點是null,數量為二個節點的總合。
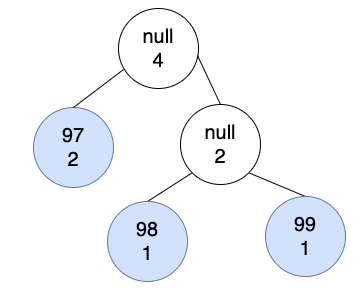
會發現葉子節點都不是null,都是有數量。
使用前序遍歷,取得葉子的編碼。根節點是空,左子樹是0,右子樹是1。
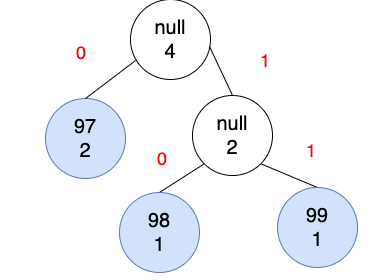
根據上圖,得到的編碼如下。
| 字母 | ASCII | 編碼 | 數量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 97 | 0 | 2 |
| b | 98 | 10 | 1 |
| c | 99 | 11 | 1 |
根據原始字串,與編碼對映,拼出編碼結果。
| 原始字串 | a | a | b | c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 編碼 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 11 |
最後產生的編碼為:
001011
將字串編碼轉成byte,byte是8個bit為一組。
由於先前範例太簡單,產生的byte,不足8bit,因此將範例改成aabbcccc。
| 字母 | ASCII | 編碼 | 數量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 97 | 10 | 2 |
| b | 98 | 11 | 2 |
| c | 99 | 0 | 4 |
| 原始字串 | a | a | b | b | c | c | c | c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 編碼 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
最後產生的編碼為:
101011110000
將字串編碼轉成byte,byte是8個bit為一組。
因此拆分為:
| byte[0] | byte[1] |
| 10101111 | 0000 |
最後一個編碼,只有4個0。
在轉換為2進位時,正數0000,就只會變成「1個」0,因此,最後會有一個空間記錄最後一位若是正整數,字串大小。
| byte[0] | byte[1] | byte[2] |
| 10101111 | 0 | 4 |
解碼
準備先前的編碼表。
| 字母 | ASCII | 編碼 | 數量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 97 | 10 | 2 |
| b | 98 | 11 | 2 |
| c | 99 | 0 | 4 |
將傳送來的byte陣列,組合原本的字串。
| byte[0] | byte[1] | byte[2] |
| 10101111 | 0 | 4 |
注意,byte陣列的最後一個元素是記錄它的前一個元素的字串大小。
把byte[1]的元素,把它補成4個0。
最後會產生以下字串。
101011110000
i變數會在索引0,另一個變數count會指向i+1,會往前走,直到找到有在編碼表的編碼。
101011110000
↑
i
↑
count
檢查索引i至count(不包含count),1是否在編碼表中?沒有的話,count++,往前移,i不動。
101011110000
↑
i
↑
count
檢查索引i至count(不包含count),10是否在編碼表中?
有,把i移到count的位置。並把10對映編碼表是a,存在list中。
101011110000
↑
i
↑
count
下一次迴圈,count是i+1,檢查索引i至count(不包含count),1是否在編碼表中?
101011110000
↑
i
↑
count
不是,count往前動,i不動。
101011110000
↑
i
↑
count
檢查索引i至count(不包含count),10是否在編碼表中?
有,把i移到count的位置。並把10對映編碼表是a,存在list中。
101011110000
↑
i
↑
count
掃完後,list中就會有對映出的字元。
建立Node
因為相加的值的節點沒有字元,是null,所以要用物件,若用byte基本型別無法設為null,byte預設為0。
1
public Byte data;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
public Byte data;
public int weight;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(Byte data, int weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
public void preOrder() {
System.out.print(this + ",");
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"data=" + data +
", weight=" + weight +
'}';
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
public class Huffman {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "I like";
byte[] bytes = content.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
List<Node> countList = count(bytes);
System.out.println(countList);
Node huffman = createHuffman(countList);
huffman.preOrder();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
getCode(huffman, "", sb);
System.out.println(huffMap);
byte[] zipbytes = zip(content.getBytes(), huffMap);
System.out.println("zipbytes:" + Arrays.toString(zipbytes));
byte[] source = decode(huffMap, zipbytes);
System.out.println(new String(source));
}
static Map<Byte, String> huffMap = new HashMap<>();
private static String byteToBitString(byte b) {
int temp = b;
temp |= 256;
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp);
// 只取倒數8位
return str.substring(str.length() - 8);
}
private static byte[] decode(Map<Byte, String> huffMap, byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// bytes.length - 1 記錄最後一個元素的字串長度
// 因為字串轉二進位,00001,前面的0都會被去掉,要記錄字串的長度,推算出前面有幾個0
// bytes.length - 2 是最後一個元素
int endIndex = bytes.length - 2;
// 注意,i小於endIndex,不處理endIndex的元素
for (int i = 0; i < endIndex; i++) {
byte b = bytes[i];
sb.append(byteToBitString(b));
}
// 處理最後一個元素endIndex
byte lastByte = bytes[endIndex];
// 若為負數
if (lastByte < 0) {
// 用原本的方式轉出
sb.append(byteToBitString(lastByte));
} else { // 若為正整數
// 先轉成二進位字串,例:0110,就會轉成110
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(lastByte);
// 取得endIndex元素的字串長度,例:0110,大小為4
byte lastCount = bytes[bytes.length - 1];
// 要使用StringBuffer.insert()插入工具
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer(str);
// lastCount = 0110原本大小為4 - 110二進位轉出來大小為3 = 1,前面還要補一個0
lastCount -= str.length();
while (lastCount > 0) {
// 在索引0插入零,之後的字串往後移
sb2.insert(0, "0");
lastCount--;
}
// 補0的字串,加在sb
sb.append(sb2);
}
Map<String, Byte> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<Byte, String> entry : huffMap.entrySet()) {
map.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey());
}
List<Byte> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < sb.length(); ) {
int count = 1;
boolean flag = true;
Byte b = null;
while (flag) {
String key = sb.substring(i, i + count);
b = map.get(key);
if (b == null) {
count++;
} else {
flag = false;
}
}
list.add(b);
i += count;
}
byte b[] = new byte[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = list.get(i);
}
return b;
}
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes, Map<Byte, String> huffMap) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (Byte b : bytes) {
sb.append(huffMap.get(b));
}
int len = 0;
if (sb.length() % 8 == 0) {
len = sb.length() / 8;
} else {
len = sb.length() / 8 + 1;
}
// +1是因為要記錄最後一個元素的大小
byte[] huffBytes = new byte[len + 1];
// 若為-1代表,最後一個元素是負數 或剛好大小就為8
huffBytes[huffBytes.length - 1] = -1;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < sb.length(); i += 8) {
String strByte = null;
if (i + 8 > sb.length()) {
strByte = sb.substring(i);
// 儲存最後一個元素的字串大小
huffBytes[huffBytes.length - 1] = (byte) strByte.length();
System.out.println("end = " + strByte);
} else {
strByte = sb.substring(i, i + 8);
}
huffBytes[index++] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
}
return huffBytes;
}
private static void getCode(Node node, String code, StringBuilder sb) {
StringBuilder sb2 = new StringBuilder(sb);
sb2.append(code);
if (node != null) {
if (node.data == null) {
getCode(node.left, "0", sb2);
getCode(node.right, "1", sb2);
} else {
huffMap.put(node.data, sb2.toString());
}
}
}
public static Node createHuffman(List<Node> list) {
while (list.size() > 1) {
Collections.sort(list);
Node leftNode = list.get(0);
Node rightNode = list.get(1);
Node node = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
node.left = leftNode;
node.right = rightNode;
list.remove(leftNode);
list.remove(rightNode);
list.add(node);
}
return list.get(0);
}
public static List<Node> count(byte[] bytes) {
List<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();
Map<Byte, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
Byte key = bytes[i];
if (!map.containsKey(key)) {
map.put(key, 1);
} else {
int count = map.get(key);
map.put(key, count + 1);
}
}
Iterator it = map.keySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Byte key = (Byte) it.next();
Integer value = map.get(key);
list.add(new Node(key, value));
}
return list;
}
}
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
public Byte data;
public int weight;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(Byte data, int weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this);
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"data=" + data +
", weight=" + weight +
'}';
}
}