共享模式
主要精神
共用的物件沒有在cache快取中,就創建一個新物件在cache,若物件有存在cache快取中,就從cache快取中抓出來。
本篇以Integer與String pool字串池作為解說。
不變與會變動
此模式很多書都用下棋解釋,這個模式要分清楚那一個是不變的,那一個是會變的,棋盤是不變的,每個玩家的下棋位置是會變的(比如圍棋黑子、白子玩家放下的位置)。
不會變的: 棋盤全部x,y座標位置。
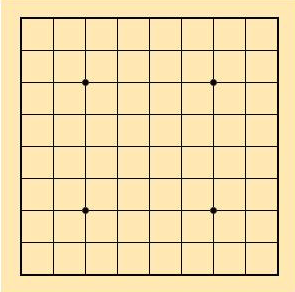
會變的: 玩家的下棋位置
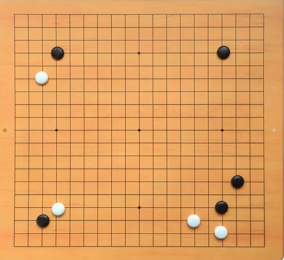
於是把棋盤全部x,y座標只存一次在cache中,假設有100場遊戲,都用cache中固定棋盤座標,而玩家下棋位置則是另外存放,才不會浪費記憶體空間,總不可能有100場遊戲,就儲存100份棋盤x,y座標+玩家下棋位置。
把可以共用的(棋盤x,y座標)抽出來共享,不能共用的,就另外儲存。
分享與不能分享
以上的案例,不變的就是可以分享的,如全部的棋盤位置,會變的就不能分享,如每個玩家的下棋位置。
Integer
以下是Integer的原始碼,Integer有一個cache快取空間,low是-128, high是127,也就是說值介於-128與127之間,就是用快取,超出這個範圍就用新的物件,目的是增加效率,不要頻繁的建立物件占用記憶體。
共享的部分是-128到127,不能共享的部分是超過範圍,就建立新的物件。
Integer.valueOf()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
//low是-128, high是127
// 介於-128至127,用快取
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
// 不是-128至127,就建立新的物件
return new Integer(i);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
private static final class IntegerCache {
// low = -128是重點!!!!
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
@Stable
static final Integer[] cache; // cache是重點!!!!
static Integer[] archivedCache;
static {
// h = 127 high = h是重點!!!! 127
int h = 127;
high = h;
CDS.initializeFromArchive(IntegerCache.class);
// 陣列大小127-(-128) + 1 = 256,所以索引0是-128,索引255是127
int size = (high - low) + 1;
// Use the archived cache if it exists and is large enough
if (archivedCache == null || size > archivedCache.length) {
// 這個是重點!!!! 建立快取!
Integer[] c = new Integer[size];
// .
// .
// .中間截掉一些程式碼
// .
// archivedCache是c陣列
archivedCache = c;
}
// cache 是 archivedCache
cache = archivedCache;
Integer比較是否相等。
以下使用new的方式已經被廢棄。
new Integer(127);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Java類型分2種,基本資料型態與物件
// 基本資料型態的比較==,比較是否相等
// 基本資料型態int, long, double, float, char小寫開頭的
// 基本資料型態的比較==,判斷「值」是否相同
System.out.println("=== 基本資料型態比較 -128 =====");
int num1 = -128;
int num2 = -128;
System.out.println(num1 == num2); // true
System.out.println("=== 基本資料型態比較 128 =====");
num1 = 128;
num2 = 128;
System.out.println(num1 == num2); // true
// Integer物件資料型態的比較,判斷是否相等
// -128至127都是指向相同物件
System.out.println("=== -128 =====");
Integer x = Integer.valueOf(-128);
Integer y = Integer.valueOf(-128);
Integer z = -128;
System.out.println(x == y); // true
System.out.println(x == z); // true
System.out.println(x.equals(y)); // true
System.out.println("=== 127 =====");
Integer x1 = Integer.valueOf(127);
Integer y1 = Integer.valueOf(127);
Integer z1 = 127;
System.out.println(x1 == y1); // true
System.out.println(x1 == z1); // true
System.out.println(x1.equals(y1)); // true
System.out.println("=== 128 =====");
Integer a = Integer.valueOf(128);
Integer b = Integer.valueOf(128);
System.out.println(a == b); // false
System.out.println(a.equals(b)); // true
}
}
=== 基本資料型態比較 -128 =====
true
=== 基本資料型態比較 128 =====
true
=== -128 =====
true
true
true
=== 127 =====
true
true
true
=== 128 =====
false
true
String pool字串池
以下字串變數指向”Jack”常數。
1
String name = "Jack";
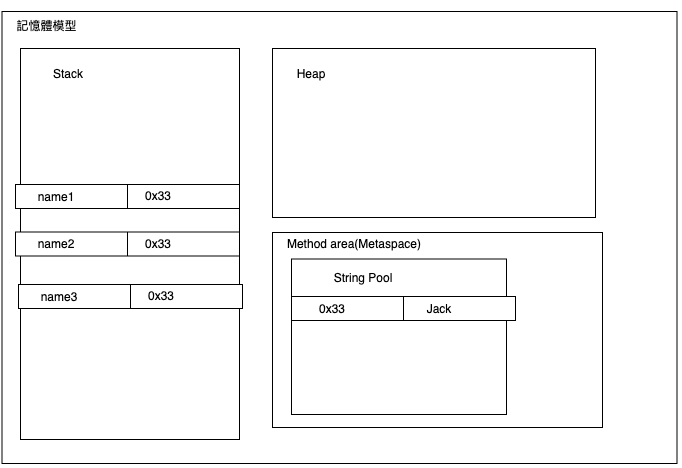
在Java memory model記憶體模型,有一個區塊是放常數,常數區塊中,又有一個區塊是放String pool字串池。
String Pool,用來儲存重複利用的字串。
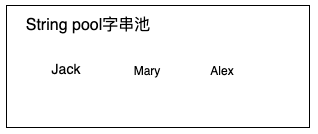
在字串池有3個常數分別是Jack, Mary, Alex
以下的程式碼比較變數的記憶體位址是否相同,結果全是true,3個變數都存放相同的記憶體位址。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name1 = "Jack";
String name2 = "Jack";
String name3 = "Jack";
System.out.println(name1 == name2); // true
System.out.println(name2 == name3); // true
}
}
true
true
下圖中,name1, name2, name3三個變數存放的是0x33的記憶體位址。
如果變數設成新的值,比如”Bill”,Bill沒有在String Pool中,就會建立一個新的字串常數,值是Bill。