Exception
什麼是例外?
什麼是例外?不正常的錯誤導致程式執行到一半停止。
以下程式碼會產生計算錯誤,因為不能除0,程式會執行到第7行時就停止,第8行以後都不執行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
package exception;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 0;
int result = num1 / num2;
if (result > 0) {
System.out.println("可以除");
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
}
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at exception.Test.main(Test.java:7)
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
告訴你錯誤原因,ArithmeticException是計算錯誤。
at exception.Test.main(Test.java:7)
告訴你程式停止在那一行,之後的程式碼就不執行了。
那要如何才能讓發生錯誤的程式碼,之後的程式碼還可以執行呢?就是要去補捉例外。
例外分類
例外分二類,分別為Error與Exception。
Error是程式設計師無法控制,Exception是程式設計師可以控管。
Error
StackOverFlow、Out of memory(OOM),Stack堆疊或Heap的記憶體被占滿,導致Crash,程序崩潰。
Stack堆疊存放變數與值是基本資料類型(int,char,byte,float,double)。
Heap存放物件,透過new關鍵字建立與物件類型一致的記憶體空間,而Stack中的變數存放的是Heap的物件記憶體位址,圖文內容請見Java Memory Model
程式(Program)是原始碼,程序(Process)是把程式碼載入到記憶體,從執行到執行完畢的一個過程,一個程式可以產生多個程序。
Exception
Exception又分為執行時例外(Runtime Exception)與編譯例外。
編譯例外
編譯例外是在寫程式時候,由編譯器檢查出來的錯誤,不是邏輯或語法錯誤,語法錯誤例如變數沒有宣告類型就使用。
語法錯誤
1
str = "Hello World!";
編譯語法
javac 檔名.java
比如IO串流程式碼,強制一定要去try-catch補捉IOException,但卻沒有去補捉,以下編譯器會在FileInputStream會有紅色底線,滑鼠移到上方,會寫Unhandled exception: java.io.FileNotFoundException
1
2
3
4
5
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("/fdfddffdf/fdfdfd");
}
}
執行時例外
執行時才發現有問題,比如發現檔案不存在,或者執行時才發現變數是null。
執行語法,注意!沒有副檔名。
java 檔名
以下指派一個不存在的檔案路徑。
1
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("/Users/cici/abdcfd");
str是null,null呼叫length(),產生NullPointException。
1
2
String str = null;
System.out.println("str len = " + str.length());
除0,會產生ArithmeticException: / by zero
1
2
3
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 0;
int result = num1 / num2;
繼承架構
Error與Exception的父類別
Object是所有類別的父類別,Throwable是Error與Exception的父類別。
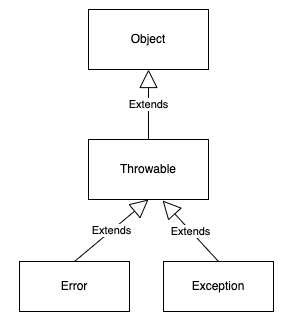
Error的子類別
Error下面有StackOverflowError與OutOfMemoryError,Exception下面有執行時例外RuntimeException。
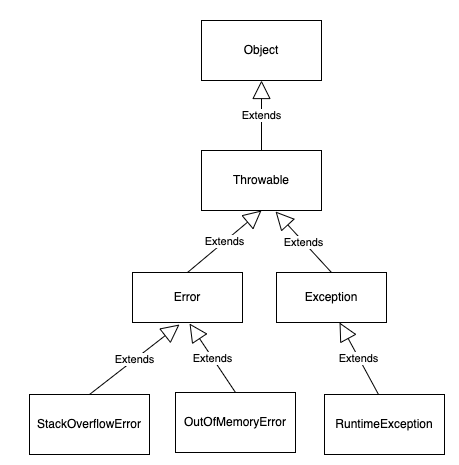
編譯例外的子類別
下圖看黃色方塊,父類別是Exception,IOException與ReflectiveOperationException是子類別。
ReflectiveOperationException下面又有
- ClassNotFoundException
- NoSuchFieldException
- NoSuchMethodException
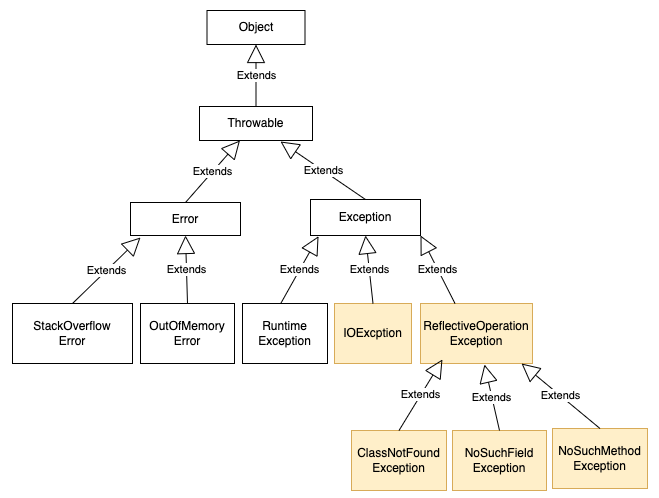
編譯例外主要針對IO串流與類別反射相關,可看IO串流與反射。
重要!!編譯例外的子類別,強制一定要補捉try-catch或拋出例外throws。
IOException的jdk文件:

ReflectiveOperationException的jdk文件:

執行時例外的子類別。
RuntimeException,沒有強制一定要補捉try-catch,不然程式碼到處都是try-catch。
RuntimeException的jdk文件:

上圖有畫底線的子類別例外如下:
- NullPointerException 有null空值
- ArithmeticException 計算錯誤
- ClassCastException 類別轉型失敗
- IndexOutOfBoundsException 超出陣列索引範圍
- NoSuchElementException 陣列中元素不存在
- IllegalStateException與IllegalArgumentException為Kotlin空值函式的類別
- NumberFormatException 無法轉換成數字
處理例外的方式
- try-catch 補捉例外,由程式設計師自己處理。
- throws 由呼叫這個方法的呼叫者自己處理。
try-catch
補捉例外,如果沒有發生例外,就不會執行catch。
語法
try {
可能會產生錯誤的程式碼
} catch (Exception e) {
1. 印出錯誤訊息
2. throw e 拋出例外
} finally {
不管有沒有例外,都會執行這個程式碼區塊
}
上述語法,第2行產生Exception的物件,會把Exception物件作為參數放在catch (Exception e)
try-catch範例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println("start"); // 1
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e); // 2
} finally {
System.out.println("finally"); // 3
}
}
}
start
null
finally
多個catch
可以有多個catch,但只會進到其中一個,且例外類別必須由子類別到父類別。
第一個catch是子類別NullPointerException,第2個catch是父類別Exception
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
try {
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("catch1: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("catch2: " + e.getMessage());
}
catch1: Cannot invoke "String.length()" because "str" is null
finally
catch多個補捉例外
要用|分開多個例外,只能使用一個變數e。
1
2
3
4
5
6
FileInputStream fis;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("/dddd");
} catch (NullPointerException | IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
有try-catch,就不用throws拋出例外
只能二選一,不能try-catch,又throws。
throws拋出例外
為什麼會有throws拋出例外?代表該方法沒有能力處理例外,所以把例外往呼叫者拋出。
jvm呼叫main()方法,main()方法呼叫func1(),func1()呼叫func2(),func2()拋出例外給呼叫者func1(),func1不try-catch,拋出例外給呼叫者main(),main()也拋出例外,jvm收到例外後,「印出錯誤訊息」然後就「停止程序」。
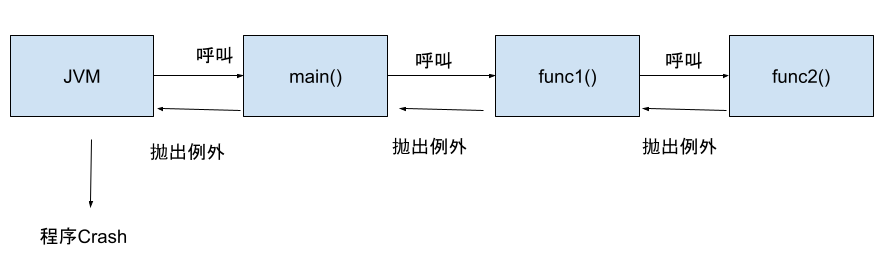
throws 後面可以是例外的父類別,或是產生例外的類別。
拋出throws FileNotFoundException。
1
2
3
4
5
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/cici/abdfdfd");
}
}
拋出父類別throws IOException
1
2
3
4
5
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/cici/abdfdfd");
}
}
throws拋出多個例外
拋出二個例外,用逗號區隔。
throws IOException, NullPointerException
1
2
3
4
5
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NullPointerException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/cici/abdfdfd");
}
}
預設throws
若程式都沒有寫try-catch,也沒有寫throws,預設會用throws拋出例外給呼叫者,至於拋出什麼例外,就看程式碼的例外而認定。
如果都沒寫try-catch,也沒有寫throws,預設會用throws。
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());
}
}
預設拋出NullPointerException。
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NullPointerException {
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());
}
}
預設拋出ArithmeticException。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ArithmeticException {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 0;
int result = num1 / num2;
}
}
子類別的throws
父類別method1()是拋出throws RuntimeException
1
2
3
4
5
class FatherException {
public void method1() throws RuntimeException {
}
}
子類別method1()也要拋出throws RuntimeException或RuntimeException子類別。
1
2
3
4
5
6
class ChildException extends FatherException{
@Override
public void method1() throws NullPointerException {
super.method1();
}
}
以下是錯誤示範,編譯不過,不能拋出Exception,因為Exception不是RuntimeException的子類別。
1
2
3
4
5
6
class ChildException extends FatherException{
@Override
public void method1() throws Exception {
super.method1();
}
}
方法的throws
IOException是屬於編譯例外,所以強制一定要處理例外,如果是RuntimeException就不用處理拋出例外,預設有throws會處理(前面有提到預設throws)。
以下程式碼會編譯錯誤,因為func1()沒有處理func2()拋出的IOException。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
func1();
}
public static void func1() {
func2();
}
public static void func2() throws IOException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/cici/abdfdfd");
}
}
如何處理?以下二擇一,try-catch或throws相同例外或throws 父類別例外。
func1() throws IOException,main() throws Exception。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
func1();
}
public static void func1() throws IOException{
func2();
}
public static void func2() throws IOException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/cici/abdfdfd");
}
}
try-catch
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
func1();
}
public static void func1() {
try {
func2();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void func2() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/cici/abdfdfd");
}
}
throw
後面沒有s,是在方法「中」,throw拋出例外。
而throws是在定義方法()後面,throws拋出例外。
語法
throw new 例外類別("錯誤訊息");
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());
if (str == null)
throw new NullPointerException("error msg = null");
}
}
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException: error msg = null
at exception.Test.main(Test.java:8)
| 拋出 | 放在那裡? | 後面是什麼 | 範例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| throws | 方法定義 | throws 類別 | public void func2() throws IOException |
| throw | 方法中 | throw new 物件(錯誤訊息) | throw new NullPointerException("錯誤") |
finally
不管有沒有例外,都要執行,常用在關閉串流,資源(檔案打開與關閉、資料庫連線、網路連線)釋放與關閉。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println("start"); // 1
String str = null; // 產生例外物件,傳入catch()
System.out.println(str.length());
} catch (Exception e) {
// 最終由Throwable父類別印出錯誤
throw new RuntimeException(e); // 2
} finally {
System.out.println("finally"); // 3
}
}
}
start
null
finally
try…finally
這個語法沒有補捉例外,一樣會crash,主要意義在於,不管執行過程有沒有例外,在程序crash前,一定要執行finally{}程式區塊。
可能用於寫Log或關閉釋放資源,什麼是資源?例如:打開檔案,讀取裡面的內容,檔案就是資源。DB資料庫連線,離開程序,要關閉DB資料庫連線,DB資料庫就是資源。網路連線,網路中斷,網路就是資源。
1
2
3
4
5
6
try {
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());
} finally {
System.out.println("程序crash前先印出這段話。");
}
程序crash前先印出這段話。
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException: Cannot invoke "String.length()" because "str" is null
at exception.Test4.main(Test4.java:11)
finally執行順序
若throw、return在try{ … } 中,finally執行順序優先throw、return
finally會先執行完,才執行throw、return
以下程式碼執行結果是什麼?程式碼中已經有寫執行順序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
func1();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 4
}
func2(); // 5
}
public static void func1() {
try {
System.out.println("func1"); // 1
throw new NullPointerException("null ptr error"); // 3
} finally {
System.out.println("func1 finally"); // 2
}
}
public static void func2() {
try {
System.out.println("func2"); // 6
return; // 8
} finally {
System.out.println("func2 finally"); // 7
}
}
}
func1
func1 finally
null ptr error
func2
func2 finally
自訂例外
可以繼承Exception與RuntimeException。
建議繼承RuntimeException,因為不會強制一定要處理例外。
例外原始碼
以下語法會呼叫一個參數(message)建構子
1
new MyNullException("錯誤訊息")
呼叫父類別一個參數(message)建構子
1
2
3
4
5
6
class MyNullException extends RuntimeException {
public MyNullException(String message) {
// 呼叫父類別一個參數(message)建構子
super(message);
}
}
最終由Throwable父類別的建構子處理message
1
2
3
4
5
public Throwable(String message) {
fillInStackTrace();
// 由detailMessage變數處理message
detailMessage = message;
}
繼承RuntimeException
main()方法不用throws Exception,會用預設的throws。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
package exception;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = null;
if (str == null)
throw new MyNullException("自訂NullException");
}
}
class MyNullException extends RuntimeException {
public MyNullException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
Exception in thread "main" exception.MyNullException: 自訂NullException
at exception.Test.main(Test.java:7)
繼承Exception
繼承Exception,強制要處理例外,方式為補捉try-catch,或者throws Exception。
main()方法要throws Exception,不然會產生編譯例外(如以下文字),無法編譯。
Unhandled exception: exception.MyNullException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
package exception;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String str = null;
if (str == null)
throw new MyNullException("自訂NullException");
}
}
class MyNullException extends Exception {
public MyNullException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
Exception in thread "main" exception.MyNullException: 自訂NullException
at exception.Test.main(Test.java:7)