extends constructor
Prerequisites:
open
Kotlin預設是不能被繼承,若要讓類別可以被繼承,在class前面加上open。
1
2
open class Parent { // 使用open class
}
父類別無主要建構式
父類別預設主要建構式
父類別沒寫主要建構子,會有一個預設的主要建構式產生。
1
2
open class Parent {
}
預設的主要建構式。
1
2
open class Parent constructor() {
}
子類別繼承父類別
子類別繼承父類別時,要呼叫主要建構式,即便父類別沒寫主要建構式,子類別還是要用父類別(),呼叫主要建構式。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 父類別沒寫主要建構子
open class Parent {
}
// 子類別繼承時要呼叫父類別的主要建構式()
class Child : Parent() {
}
父類別有主要建構式
1
2
open class Parent(val name: String, val age: Int) {
}
子類別繼承父類別
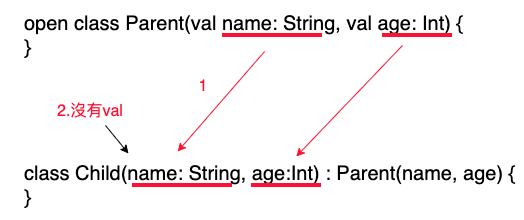
- 子類別要把父類別的建構式的參數,寫在子類別的主要建構式中。
- 子類別主要建構式的參數若跟父類別參數一樣,前面不能有val、var,因為父類別已經宣告過了,不用再加上val、var。
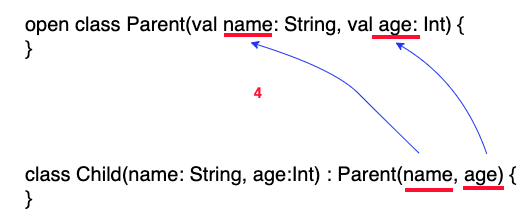
- 把子類別主要建構式的參數,代入繼承父類別建構式中。
- 參數會代入父類別的主要建構式。

1
2
class Child(name: String, age:Int) : Parent(name, age) {
}
為什麼要這樣做?因為繼承的時候,要呼叫父類別的主要建構式,建立父類別屬性。
就像Java中,子類別繼承父類別,預設會呼叫super(),建立父類別。
子類別沒有主要建構式
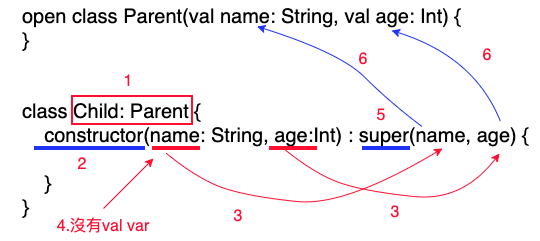
若子類別沒有主要建構式,要在次要建構式中,使用super,呼叫父類別的主要建構式。
步驟如下:
- 繼承,不用 : 父類別(參數, 參數),直接 : 父類別
- 使用constructor關鍵字,建立次要建構式。
- 把父類別的主要建構式的參數,寫在子類別的次要建構式中。
- 子類別次要建構式的參數,前面不能有val、var,次要建構式參數本來就不能加val、var。
- 使用super關鍵字,把子類別次要建構式的參數,代入繼承父類別建構式。
- 參數會代入父類別的主要建構式。
1
2
3
4
class Child: Parent {
constructor(name: String, age:Int) : super(name, age) {
}
}
繼承父類次要建構式
父類別有主要建構式和次要建構式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
open class Parent(val name: String, val age: Int) {
var hobby: String = ""
constructor(name: String, age: Int, hobby: String) :
this(name, age) {
this.hobby = hobby
}
}
子類別繼承呼叫父類次要建構式。
1
2
3
4
5
class Child : Parent {
constructor(name: String, age: Int, hobby: String) :
super(name, age, hobby) {
}
}
父類別沒有主要建構式
1
2
3
4
open class Parent {
constructor(name: String) {
}
}
子類別繼承呼叫父類次要建構式。
1
2
3
4
class Child : Parent {
constructor(name: String) : super(name) {
}
}
主要建構式權限修飾子
若主要建構式有權限修飾子,要把constructor寫出來,次建構式要用this()呼叫主要建構式。
1
2
3
4
open class Parent protected constructor() {
constructor(name: String) : this() {
}
}
結論
不管如何,都要繼承其中一個父類建構式,管它是主要建構式或次要建構式,一定要繼承其中一個。