coroutineScope
coroutineScope開頭字母為小寫。
使用時機
- 在 suspend 函式內,「順序執行」 或 「同時執行」(需搭配launch/async) 多個任務。
- 任務必須為suspend函式。
2個任務
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// 第1個任務
private suspend fun doOne():Int {
// 1秒
delay(1000)
return 10
}
// 第2個任務
private suspend fun doTwo():Int {
// 1秒
delay(1000)
return 20
}
順序執行
以下程式碼,二個函式是順序執行,先執行doOne(),再執行doTwo(),執行時間是2017 ms。
coroutineScope會等待子協程(doOne,doTwo),順序執行完畢。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
fun coroutin05() = runBlocking {
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
coroutineScope {
val one = doOne()
val two = doTwo()
}
val duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime
println(" in ${duration} ms")
}
in 2017 ms
同時(並行)執行
「同時執行」(需搭配launch/async) 多個任務,以下執行秒數為1秒,代表是同時執行與結束。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@Test
fun coroutin05() = runBlocking {
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
coroutineScope {
val one = launch{doOne()}
val two = async{doTwo()}
}
val duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime
println(" in ${duration} ms")
}
in 1021 ms
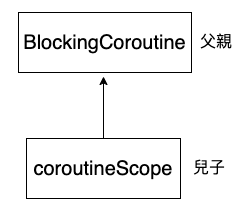
coroutineScope 與 runBlocking
coroutineScope的父親是runBlocking,因為是父子關係,所以runBlocking會等待coroutineScope{}中的子任務執行完畢,runBlocking才執行完畢。
不必使用join(),runBlocking就會自動等待coroutineScope{}。
CoroutineScope 與 runBlocking
CoroutineScope的父親不是runBlocking,所以要使用join(),讓runBlocking等待CoroutineScope執行完畢,才能結束。
若不加上join(),runBlocking{}就會先結束,而不會等待CoroutineScope執行完畢。
runBlocking協程「等待」scope.job完成,runBlocking才能結束。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
fun coroutin07() = runBlocking {
val scope = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default)
val job = scope.launch {
delay(1000)
println("job1")
}
job.join()
}
job1