Stack實作
Stack是在同一個位置新增/刪除的動作。
新增在頭節點
Stack是新增節點在頭節點。
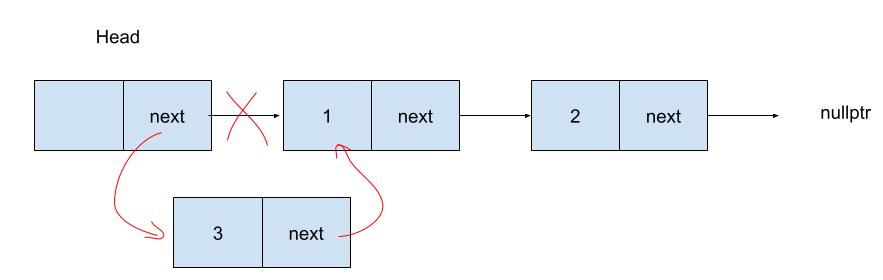
刪除在頭節點
Stack是刪除節點在頭節點。
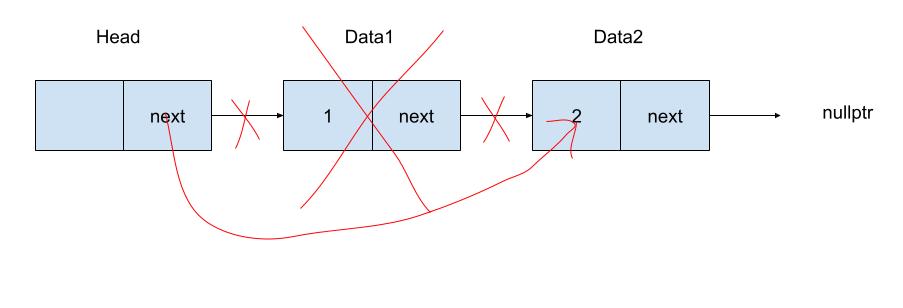
函式解釋
Stack的新增,等同於鏈結串列的addFirst,此處改為push
Stack的刪除,等同於鏈結串列的removeFirst,此處改為pop
程式碼與單向鏈結串列大致相同,刪除以下描述的函式。
新增在最後addLast(),插入在某個節點前面insert(),以上二種函式在Stack中都不需要。
刪除在最後removeLast(),刪除在某個節點deleteNode(),以上二種函式在Stack中都不需要。
getNode(),取得節點的函式,在Stack中也不需要。
pop
對Stack來說,刪除鏈結串列第1個節點之外,還要把值返回。 所以以下的程式碼參數有ElemType& e,接收刪除後返回值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
bool pop(Node* head, ElemType& e) {
if(head == nullptr) {
cout << "鏈結串列不存在" << endl;
return false;
}
//只有頭節點,沒有後面的資料
if(head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "沒有任何節點" << endl;
return false;
}
//不包含頭節點,取得頭節點的下一個
Node* p = head->next;
//頭節點的下一個是 p的下一個
head->next = p->next;
//p的下一個節點的prev是頭節點
p->next->prev = head;
e = p->data;
//把p刪掉
delete p;
return true;
}
完整程式碼
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
using namespace std;
typedef int ElemType;
//定義節點
struct Node {
ElemType data;
Node *prev,*next;//前面節點與後面節點
};
/**
初始化鏈結串列
*/
Node* initLinkedList() {
//頭節點
Node* head = new (std::nothrow)Node;
//頭節點記憶體分配失敗
if(head == nullptr) return nullptr;
//前面節點與後面節點全設為nullptr
head->prev = head->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
/**
鏈結串列記憶體回收
參數為頭節點
*/
void destroyLinkedList(Node* head){
if(head == nullptr) {
cout << "鏈結串列不存在" << endl;
return;
}
Node *temp; //暫存節點
//繞行鏈結串列
while(head != nullptr) {
//先把下一個節點存起來
temp = head->next;
//刪掉目前的節點
delete head;
//把剛才存下來的節點作為頭節點
head = temp;
}
}
bool push(Node* head, const ElemType& ee) {
if(head == nullptr) {
cout << "鏈結串列不存在" << endl;
return false;
}
//建立新節點
Node* temp = new (std::nothrow)Node;
if(temp == nullptr) return false;
//新節點設定傳進來的資料
temp->data = ee;
//新節點的下一個節點是頭節點的下一個
temp->next = head->next;
//前面節點
temp->prev = head;
//頭節點的下一個是新節點
head->next = temp;
//下一個節點的前面節點,指向新建的節點
if(temp->next != nullptr)
temp->next->prev = temp;
return true;
}
void printList(const Node* head) {
if(head == nullptr) {
cout << "鏈結串列不存在" << endl;
return;
}
//從head的下一個節點開始
//head不存在值
Node *p = head->next;
while(p != nullptr) {
cout << p->data << ",";
//節點p換成下一個節點
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
size_t size(Node* head) {
if(head == nullptr) {
cout << "鏈結串列不存在" << endl;
return 0;
}
//不包含頭節點
Node* p = head->next;
size_t size = 0;
//繞行到null
while(p != nullptr) {
p = p->next;
size++;
}
return size;
//遞迴方式
//if(head == nullptr) return 0;
//return size(head->next) + 1;
}
bool pop(Node* head, ElemType& e) {
if(head == nullptr) {
cout << "鏈結串列不存在" << endl;
return false;
}
//只有頭節點,沒有後面的資料
if(head->next == nullptr) {
cout << "沒有任何節點" << endl;
return false;
}
//不包含頭節點,取得頭節點的下一個
Node* p = head->next;
//頭節點的下一個是 p的下一個
head->next = p->next;
//p的下一個節點的prev是頭節點
p->next->prev = head;
e = p->data;
//把p刪掉
delete p;
return true;
}
int main() {
//建立頭節點
Node* stack = initLinkedList();
//增加節點
push(stack, 1);
//增加節點
push(stack, 2);
//增加節點
push(stack, 3);
//增加節點
push(stack, 4);
//印出所有節點
printList(stack);
ElemType e;
pop(stack,e);
cout << "pop 的值 = " << e << endl;
//釋放記憶體(包含頭節點)
destroyLinkedList(stack);
return 0;
}